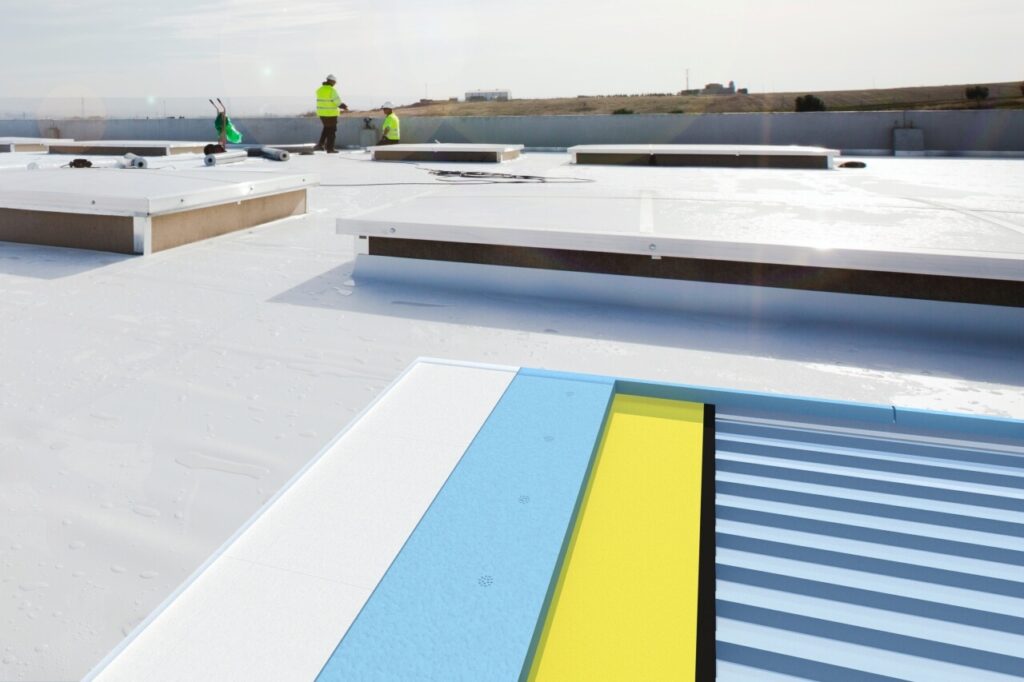
Insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption in buildings. Several types of insulation materials are available in the market, each with its own set of characteristics and advantages. For this article, the DANOSA blog team have explored five popular insulation materials: PIR, mineral wool, vacuum insulation panels (VIPs), expanded polystyrene (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS) insulation.

PIR (Polyisocyanurate) insulation is a type of rigid foam board widely specified in the warm roof buildups of residential and commercial buildings. It offers excellent thermal insulation properties. PIR insulation boards consist of a closed-cell foam core, which provides low thermal conductivity. This means that PIR insulation can effectively reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, PIR insulation is lightweight and easy to install, making it a preferred choice for various applications. However, PIR is not suitable for heavy access or foot traffic, so it shouldn’t be specified for terraces.
Mineral wool insulation is made from either natural or synthetic minerals. It is commonly available in the form of batts, rolls, or loose-fill. Mineral wool insulation has excellent fire resistance properties and is highly effective at reducing sound transmission. It provides good thermal insulation by trapping air in its fibrous structure, but isn’t the most thermally efficient solution compared to other insulations in this article. It’s important to consider that the boards are heavy and can be difficult to handle. This insulation is suitable for maintenance foot traffic only.
Vacuum insulation panels (VIPs) are a relatively new type of insulation material. They consist of a rigid core, typically made of fiberglass or silica, enclosed in an airtight barrier. The core is evacuated to create a vacuum, which significantly reduces heat transfer by eliminating the air molecules that conduct heat. VIPs offer excellent thermal insulation performance with very low thermal conductivity. Due to their thin profile, they are particularly useful in situations where space is limited. However, VIPs are relatively expensive and require careful handling to maintain their vacuum integrity; this means they can’t be mechanically fastened and aren’t suitable for areas of heavy access or foot traffic.
EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) insulation is made from expanded polystyrene beads that are fused together to form rigid panels or boards. These panels have a closed-cell structure, which traps air and reduces heat transfer, making it an effective insulator. EPS insulation is lightweight, easy to handle, and can be easily cut to fit various shapes and sizes, making it easy to create falls in tapered insulation schemes. Additionally, EPS insulation is environmentally friendly as it can be recycled and has a low impact on the ozone layer.
XPS (Extruded Polystyrene) insulation is another widely used option for thermal insulation. XPS insulation is made by extruding polystyrene through a process that creates a closed-cell foam structure. This closed-cell structure provides excellent thermal resistance and prevents the passage of air, making XPS insulation highly effective in reducing heat loss or gain. XPS insulation is also moisture-resistant, making it suitable for applications in areas prone to water exposure, such as basements or below-grade installations, as well as inverted roof systems. It offers high compressive strength, making it ideal for insulating foundations or roof terraces that can expect a lot of traffic. Additionally, XPS insulation is durable, long-lasting, and can be easily installed using adhesive or mechanical fasteners. However, it’s important to note that XPS insulation is not biodegradable and requires proper disposal to minimise its impact on the environment.
When loading directly onto a roof system, the insulation is the key component of the waterproofing system to consider:
| Insulation | Point Loading Compressive Strength at 10% (kPA) | Static Dead Loading: Evenly Distributed Maximum Supported Load (kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| PIR (Polyisocyanurate) | 150 | 30 (3,000kg/m2) |
| Mineral Wool | 80 | 16 (1,600kg/m2) |
| Vacuum Insulation | 150 | 30 (3,000kg/m2) |
| EPS (Expanded) | 150-500 | 30-100 (3,000kg/m2 – 10,000kg/m2) |
| XPS (Extruded) | 300-500 | 60-100 (6,000kg/m2 – 10,000kg/m2) |
In conclusion, PIR, mineral wool, vacuum insulation panels (VIPs), and EPS and XPS insulation are all effective materials for thermal insulation in buildings. Each material offers its own unique advantages, such as high fire resistance, acoustic insulation, and moisture resistance. The choice of insulation material depends on various factors, including the specific application, budget, desired thermal performance, and local building codes. Consulting with a professional or conducting a thorough analysis of the building’s requirements can help determine the most suitable insulation material for a given project. Speak to us on +44 (0) 845 074 0553 or uksales@danosa.com and a member of our team would be happy to create a specification for your project.